巨大タンパク質のギネス記録更新?
巨大なタンパク質として、しばしば言及されるのは、ヒトを含めた動物の筋肉に含まれる約40000個のアミノ酸からなるTitinです。一般的には、2000個のアミノ酸からできているタンパク質でも「大きな」タンパク質という感覚だと思います。
このほど、カリフォルニア大学バークレー校の計算生物学者のチームが、Titinの2倍を超える85000アミノ酸の巨大タンパク質を含む、さらに大きなタンパク質を数十個発見し、bioRxivに査読前のプレプリントとして11月22日に掲載しています。
巨大タンパク質に関する包括的な調査では、2008年に発表されたものがあり、細菌やアーケアのゲノムには、非常に大きなタンパク質をコードする遺伝子が存在する可能性が示唆されてきました。
今回、巨大タンパク質が見つかったのは、Omnitrophotaと呼ばれる小さな細菌のゲノム解析の結果です。Omnitrophotaは、1990年代に米国イエローストーン国立公園でDNAの短い断片に基づいて発見されました。実験室で成長させることができなかったため、Omnitrophotaは「微生物の暗黒物質」であると言われてきました。しかし、最近、ドイツのマックス・プランク海洋微生物研究所のグループが、地熱環境、淡水湖、廃水、地下水、泉などさまざまな試料からOmnitrophotaを見つけ、ほとんどが450nm未満の大きさのこれらの細胞を濃縮する方法を開発し、分析することに成功しました。
今回のカリフォルニア大学バークレー校のチームによる発見は、こうした情報の結果にもとづくもので、85,804個のアミノ酸からなるタンパク質を含む、30,000アミノ酸より長いタンパク質をコードするOmnitrophota遺伝子を合計46個発見しています。
例えば、タンパク質SR-VP_9_9_2021_34_2B_1_4m_PACBIO-HIFI_HIFIASM-META_416_C_1924の予測されるドメイン構造には、細胞膜を複数回通過するセグメントや、接着や糖鎖分解に関与すると考えられるものが見られます(下図)。単位が、kAA(キロ・アミノ酸)であることに注意してください。
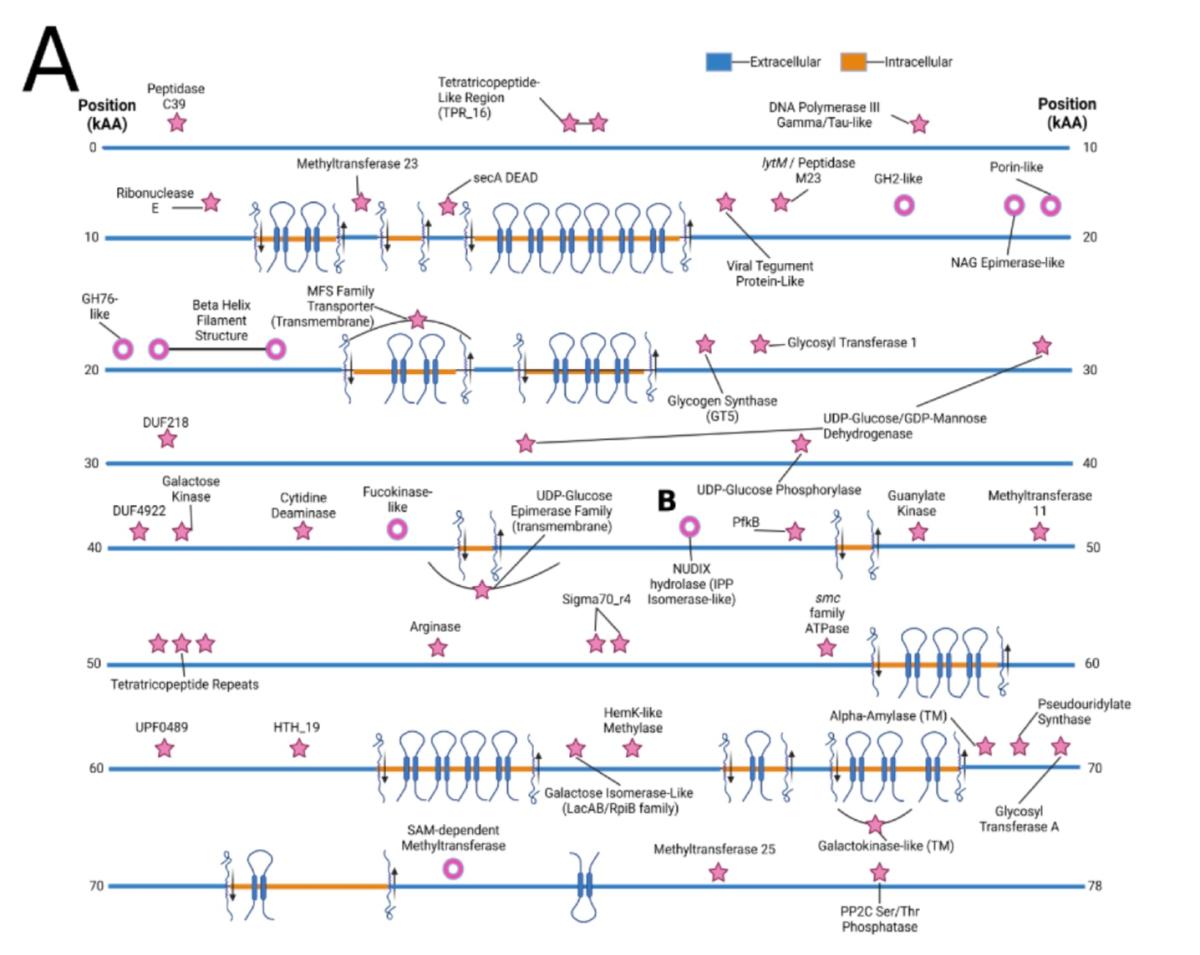
Omnitrophotaゲノムに含まれる巨大遺伝子の多くは、II型分泌系および糖質輸入に関わる遺伝子と相同な配列をもつ遺伝子に近接して存在しています。
アミノ酸配列からタンパク質の構造を予測するDeepMindの人工知能プログラムAlphaFoldを使った結果、多くの細胞壁結合領域が明らかになりましたが、非常に長いチューブ状の構造が予測されたとのことです。 これらのことから、こうしたOmnitrophotaの巨大タンパク質が、他の微生物を捕食する際に、接着と細胞壁の消化を可能にしていることが推定されるとしています。
しかし、実際にこのような巨大タンパク質が本当にこのような分子として存在、機能しているのかは不明であり、分解されて機能したりしている可能性もあり、本当の姿はまだ不明のままです。
【Twitter】 https://twitter.com/yamagatm3
更新の通知を受け取りましょう
























投稿したコメント