進むミクロスケールのコネクトームの公開
コネクトーム(connectome)は、神経系のすべての神経細胞が接続することでできた神経回路の全体のことです。このところ、このようなデータベースの公開についての発表が相次いていますので、紹介したいと思います。電子顕微鏡で撮影した神経系をビジュアルに見やすいように描き出すことで、神経系の成り立ちを理解しようとするものです。とりあえず、YouTubeでの動画を見て、神経系を眺めてみるということでお楽しみください。こういう構造を作ったり、操作したりするのが、合成生物学の未来となると思います。
📌ショウジョウバエ視覚系
バージニア州にあるHHMI Janelia Research Campusの研究チームは、ショウジョウバエの視覚系を構成する 50,000 個を超えるニューロンの包括的なマップであるコネクトームを公開しました(bioRxiv、4月18日)。 このデータは、視覚がどのように機能するかについての理解を深め、人間の視覚システムなどのより複雑な視覚システムを理解するのに役立ちます。 コネクトームは、高解像度の電子顕微鏡とコンピューター分析を使用して作成されました。
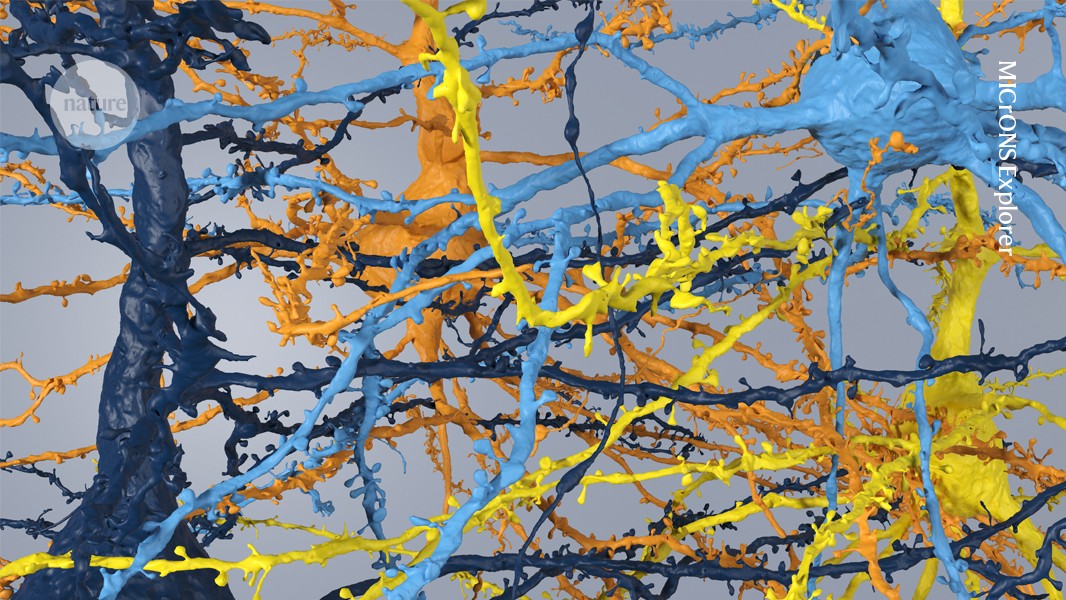
📌マウスMICrONSプロジェクト
国際的な研究チームである「Machine Intelligence from Cortical Networks (MICrONS) プログラム」は、マウスの視覚野の立方ミリメートル領域の3D電子顕微鏡による再構成と、同じ領域からのニューロン活動の蛍光イメージングに成功しました。これは、脳の複雑な構造と機能の理解において画期的な成果です。
この研究は、脳のシナプスレベルの組織を解明し、臓器の多くの機能を調整する回路を図示することを目的とした「コネクトミクス」分野における重要な一歩です。得られたデータは、神経科学コミュニティにとって貴重なリソースとなるだけでなく、人工知能の開発にも役立つ可能性があります。
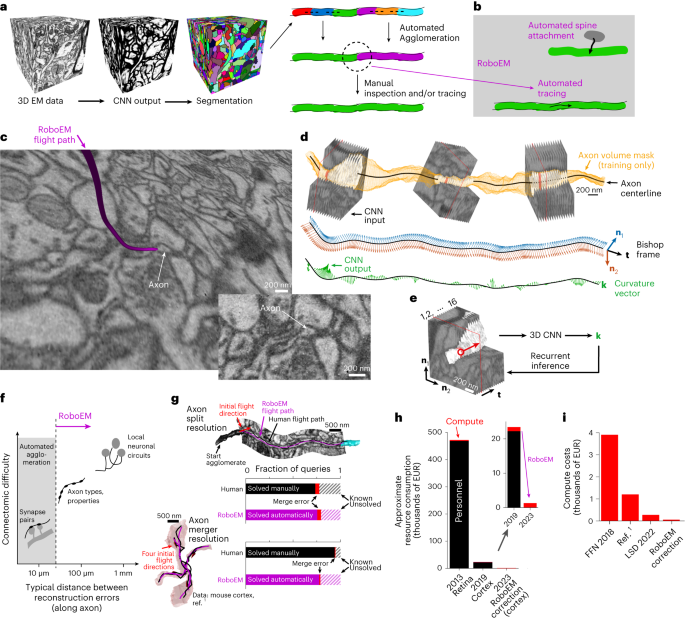
Schmidt, M. et al. (2024) RoboEM: automated 3D flight tracing for synaptic-resolution connectomics. Nat Methods
しかし、これはまだ脳全体のほんの一部分にすぎません。研究者たちは、脳全体をマッピングし、その仕組みを完全に理解するためには、さらなる技術革新と資金が必要です。
MICrONS Explorer
【合成生物学ポータル】 https://synbio.hatenablog.jp
【Twitter】 https://twitter.com/yamagatm3
更新の通知を受け取りましょう






















投稿したコメント